Data Analytics for Business: Data Modeling Variations
In the last two editions of the Data Analytics for Business at The FinData Lake Newsletter, we shed light on two important questions in the workplace: How to incorporate Data-Driven Change and How Data Can Improve Business Revenue. We’ve focused on the aspect of changing business environments and how we can utilize internal decision support systems and their benefits to organizations, as well as primarily discussing the five key indicators that guarantee returns through the implications of data analytics on your business workflow.
After reading the first and second editions, you were able to go on the road of understanding the detailed technical backbone of data analytics and how it can be used strategically to improve your business’s digital transformation phase, as well as conceptualize different approaches to the real usage of data analytics for business stakeholders and senior management.
Furthermore, our new edition will be discussing the technical side of what could be described as “the know-how to process and present your raw data.” which most people refer to as “What is Data Modeling?!”
📖 DEFINITION OF DATA MODELING
Data modeling is a process used to define and analyze data requirements needed to support the business processes within the scope of corresponding information systems in organizations. Therefore, the process of data modeling involves professional data modelers working closely with business stakeholders as well as potential users of the information system.
Source: Wikipedia
🔎PERCEPTION OF DATA MODELING TODAY
Data modeling is very underrated in today’s business world. Almost a few businesses and SMEs are using proper data modeling techniques by professional data analysts/scientists in order to turn their raw data into a real visualization that translates their business efforts or forecasts their future actions.
People tend to think of data modeling as being either just an excel worksheet that presents two columns or an advanced machine learning algorithm that is only developed by someone like Bill Gates.
Although data modeling is perceived from multiple dimensions depending on the work environment and scope, what we will discuss today is the basics of data modeling to visualize raw data and answer business questions.
⏹️ THE GOLDEN SQUARE OF DATA MODELING AND ANALYTICS
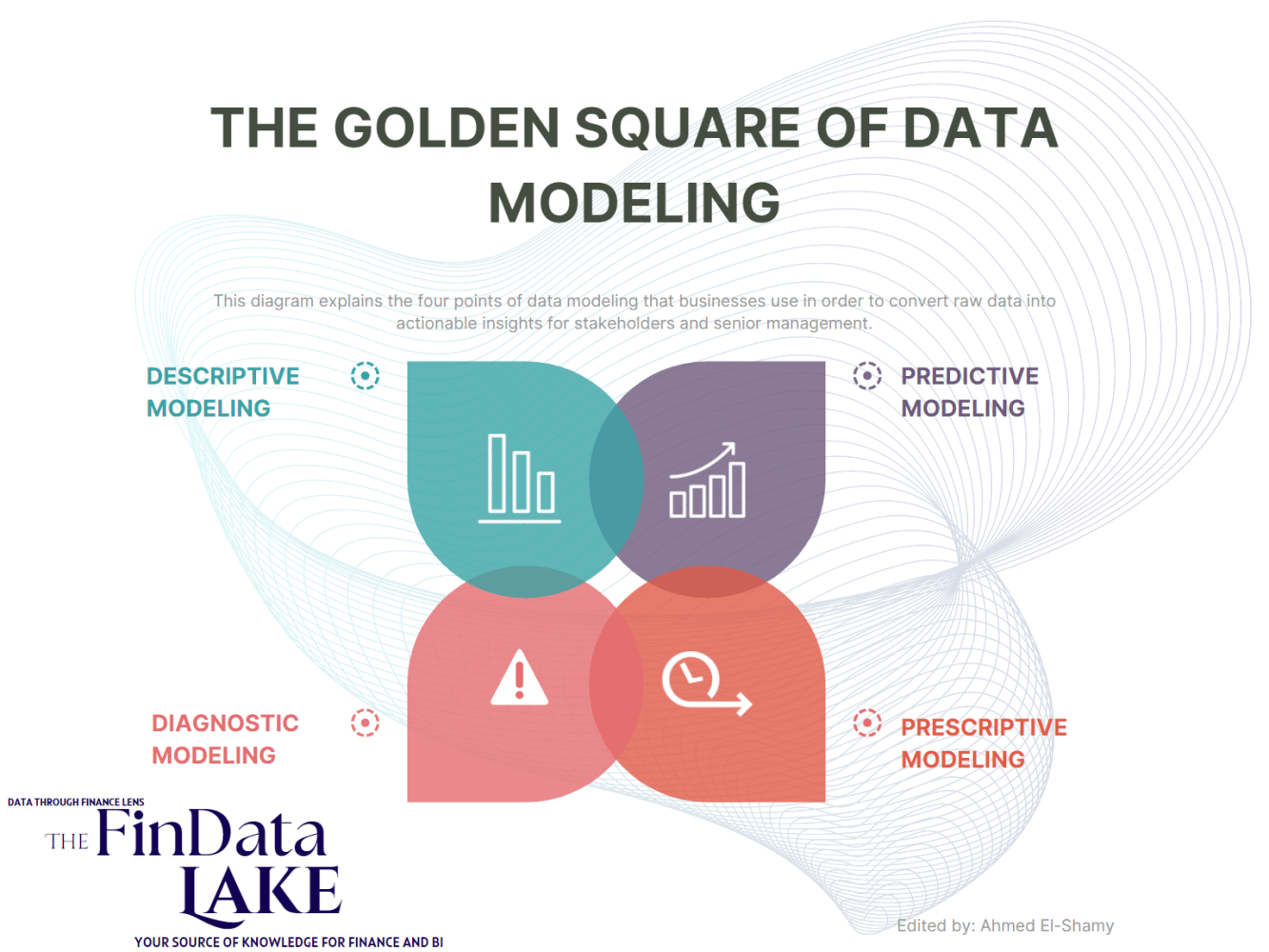
This diagram explains the four points of data modeling that businesses use in order to convert raw data into actionable insights for stakeholders and senior management.
→ Descriptive Modeling:
📊Descriptive Modeling is the process by which data analysts and scientists present historical data to senior management and stakeholders to analyze the previously-set outcome of decisions taken during a given period of time in a business segment or division. It has no involvement in predicting or forecasting what will happen in the future.
Descriptive modeling is being used in today’s businesses mostly. Your role as a business owner or a manager is to constantly seek updates on your business’s metrics in the past to decide what will be adjusted in the future.
Examples of Descriptive Modeling: Answering sales questions (Total quantities sold, Aggregated Transactions, Operations Cost, etc.)
→ Diagnostic Modeling:
⚠️Diagnostic Modeling is phase two of Descriptive Modeling. In Descriptive modeling, we’ve agreed on the fact that it is only used to process data from a historical point of view. aka just presenting a final number; diagnostic modeling, on the other hand, is showcasing the “Why?” behind those numbers; hence the name “diagnostic”.
An example would be: examining market demand; explaining customers’ behavior; identifying IT issues; and improving company culture.
/Catherine Cote has written a great article showcasing more info on the given examples presented in detail at Harvard Business School./
→ Predictive Modeling:

📈Predictive Modeling is the method used by data scientists to predict certain events based on current data assets.
It gives more insights and opens more questions about what will happen in the near or far future for senior management and stakeholders to understand the bigger picture and have different decision plans to be used whenever one or more events occur based on current analytics.
Basically, it is used to save all possible scenarios that may or may not happen to a business and to save those plans for action by those in charge to take fast calls and mitigate potential risks, if any. But it is not used alone! You’re just building layer bricks for your perspective analytics findings.
→ Prescriptive Modeling:
⌛Prescriptive Modeling is the total opposite of diagnostic modeling. When you analyzed the causation behind your descriptive modeling results through the diagnostic modeling approach, you only wanted to care about the reason why something happened in the past.
Whereas in prescriptive modeling, you’ll use the result of your predictive modeling approach in order to draw multiple scenarios and events that conclude your predicted outcome; to help and assist you in your future decision-making whenever a specific event occurs.
There is a great definition of Prescriptive Analytics that was posted by Investopedia that I wanted to quote with all of you today.
“Prescriptive analytics is a type of data analytics—the use of technology to help businesses make better decisions through the analysis of raw data. Specifically, prescriptive analytics factors in information about possible situations or scenarios, available resources, past performance, and current performance, and suggests a course of action or strategy. It can be used to make decisions on any time horizon, from immediate to long-term. “
In other words, it’s the cherry-on-top for all of the above processes. It visualizes one or more modeling assets to be presented to decision-makers.
🤖 USED TOOLS AND MODELING AUTOMATION
1️⃣Microsoft Excel
It’s the king of all spreadsheet editing and modeling software. Used by almost every facility/institution/organization/corporate or bank across the globe. But at the end of the day, old is old. And technology is rapidly moving forward! That’s why Microsoft had to step in to develop Power Query in order to implement it into Excel, and further in time, they decided to duplicate its mechanism with a prime focus on visualizing and modeling data from multiple sources into the all-new Microsoft Power BI.
2️⃣Microsoft Power BI Desktop
Power BI is an interactive data visualization software product developed by Microsoft with a primary focus on business intelligence. It is part of the Microsoft Power Platform. It is capable of grabbing data from hundreds of data sources to be processed and manipulated by developers to achieve their organization’s goals. The Microsoft team is focusing heavily on it, and they have a monthly schedule update for it!
You can publish your reports on the Microsoft Cloud for stakeholders and senior management through an interactive link to be shared without the usage of the software itself (Accessible via mobile too!)
3️⃣Google Charts
Google Charts is a free web-based alternative. It has a variety of charts to be used within its gallery, HTML5 implementation, Dynamic Data Connection, Controls, and Dashboard Visualization.
Google has set up a complete walkthrough guide for newcomers to make sure that users know all of its capabilities.
It has the highest number of visualization sets available for a free tool. You can check out all of its features in the below link.
4️⃣IBM Watson Studio
IBM Watson Studio is a very underrated tool that was created by IBM. Previously, it was named Data Science Experience, or IBM DSE. It includes over 300 built-in applications to be utilized by data analysts and scientists for data visualization, data regression, data manipulation, machine learning, AI-based computing, etc.
It’s not free, but you can get access to it if you’re a student of the IBM Data Analyst or IBM Data Scientist Certification Programs. They include a free month’s access to understand how the Watson studio performs and to create real-world data modeling projects by hand.
5️⃣Tableau Desktop
There is no tool in the market that visualizes data better than Tableau Desktop. It gained its fame when it was released for its capability to integrate with Salesforce applications.
I haven’t used Tableau Desktop that much but I can tell by the feedback I received previously from people that worked with it, that it’s a very strong visualization tool. And it has a lot of free tutorials on YouTube to guide young analysts through the process of visualizing their data properly.
You can follow up on the commonly used tools of data modeling and its technical background here in my article that discusses the Top 5 Must-Have Technical Skills for Data Scientists/Analysts.
🛫 THE TAKEAWAY
You’ve now learned the difference between different data modeling techniques. There are four data modeling concepts: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics modeling. You’ve gone through a summary of the details for the top-used software available on the market for data modeling and data processing automation. And you should have grasped a good foundational concept of what a data analyst or scientist can do for your business to improve your day-to-day activities as well as boost your revenues and mitigate its risks by offering multiple scenarios with its solutions to be used when needed.
After you’ve understood the foundation of the data modeling, we’ll discuss its visible implications in the next article of the FinData Lake Newsletter.
❔Thoughts
Tell me what you think of the current data visualization status across businesses. What can be improved further, from your point of view? And do you think that the currently available software in the market offers a solution to the problem businesses face today?